

When done editing the hosts file, press control-o to save the file. #72.249.5.10 # sign comments out an entry in the HOSTS file. Once you don't need the entry, you can either comment it out or delete it. Įach subdomain like, has to be entered seperately to the HOSTS file.ħ2.249.5.10 The above entry will force your PC's DNS for to 72.249.5.10 instead of the live site. Syntax: HOST IP DomainName DomainName DomainName. You can navigate the file using the arrow keys. Or edit one of the default values if you know what you are doing! Simply append your new mappings underneath the default ones. The hosts file contains some comments (lines starting with the # symbol), as well as some default hostname mappings (e.g. Open the hosts by typing on the Terminal that you have just opened: to redirect domains to local addresses.Įither by start typing Terminal on the Spotlight, or by going into Applications -> Utilities -> Terminal. The hosts file can be edited to block certain hostnames (like ad-serving/malicious hosts), or used for web development purposes, i.e. Upon typing a url address on the browser, the system is checking if there is a relevant entry on the hosts file and gets the corresponding IP address, else it resolves the IP via the active connection’s DNS servers. The hosts file is a text file that maps hostnames to IP addresses.
Hosts file mac os x mac os x#
Do not change this entry.Ģ55. Essentials - 3Essentials Hosting How To: Edit HOSTS file on Mac OS X
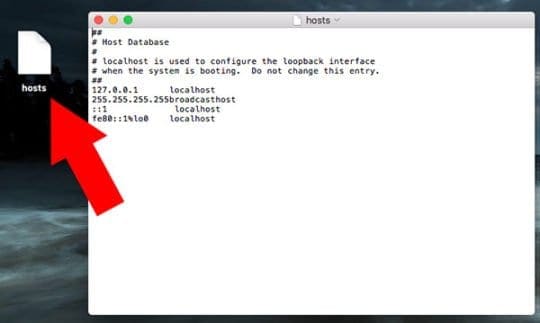
# localhost is used to configure the loopback interface
Hosts file mac os x how to#
If you ever make a mistake and you’re not sure how to fix it, you can always restore the default hosts file contents by using one of the methods above to enter the following default information: Our examples mentioned blocking and redirecting distracting sites in a work environment but you can also use these steps to manually block access to malicious websites and, of course, other uses as well.
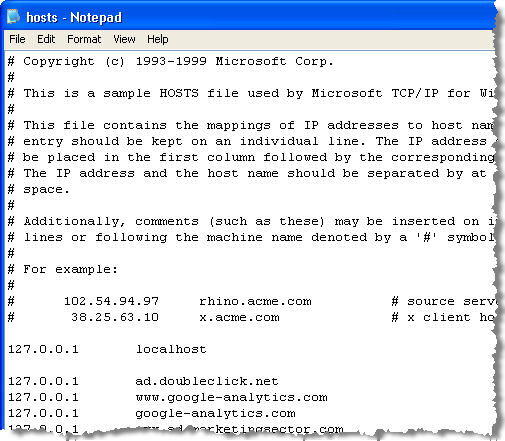
When you’re done making changes, press Control-X to exit the editor, Y to save, and Return to overwrite the existing hosts file.Īs we mentioned earlier, make sure to flush your DNS cache if you notice that your new mappings aren’t working properly. Because we launched Nano using sudo, any changes will be authenticated and saved directly to the original hosts file, without the need to copy it outside of its home directory.Ĥ. Just as we did with the TextEdit method above, we can add, edit, or remove hostname mappings at will. To navigate and edit the file in Nano, use the arrow keys on your keyboard.ģ. You’ll now see the hosts file open in the Nano editor or vim or another editor of your choice.
Hosts file mac os x password#
As with all sudo commands, you’ll need to also enter your admin password to execute it: " sudo nano /private/etc/hosts“Ģ.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
